


ElectromagnetsWe defined POWER as the RATE of doing work. The actual work or capacity to do work is called ENERGY . Energy can be Kinetic (dynamic), Potential (static), or Radiant (electromagnetic) in nature. Energy, according physical law of "Conservation of Energy", is never lost nor gained. It may be changed from one form to another, but it never just "disappears". Just like in our resistor, we had energy being used which was dissipated as heat. The electrical energy was transformed into heat energy. It didn't disappear, it merely changed form. There are many other forms of energy. Some other forms of energy are light, sound, momentum, and MAGNETISM . We are all familiar with magnets, and their peculiar properties which make them seem almost magical. A magnet can be used to hold a screw onto a screwdriver, to lift a car, or find your way in the forest. But what is it that makes a magnet do what it does? 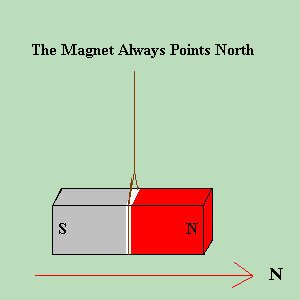 If we take a magnet, and mark one end of it, we can identify one end from the
other. If we then suspend the magnet from a string, so that it is free to
rotate, we will notice that one end will ALWAYS point toward the north, and
that it will ALWAYS be the same end of the magnet that points north.
If we take a magnet, and mark one end of it, we can identify one end from the
other. If we then suspend the magnet from a string, so that it is free to
rotate, we will notice that one end will ALWAYS point toward the north, and
that it will ALWAYS be the same end of the magnet that points north.
From this, we have concluded that there is a NORTH POLE and a SOUTH POLE on every magnet. Typically the north pole is marked with an N, and south pole is marked with an S. Now if we take two magnets with known, marked poles, and bring the North Pole of one magnet close to the South Pole of the second magnet, the two magnets will PULL TOWARD one another until they are connected. If we reverse the experiment, and bring the North Pole of one magnet, near the North Pole of the second magnet, they will PUSH AWAY from each other. 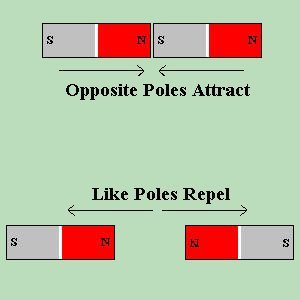 This effect is called the
LAW OF POLES
which states:
This effect is called the
LAW OF POLES
which states:
Why is it that magnets act this way? And why do magnets have poles? These are questions which science has found difficult to answer. It is believed, though, that according to the Molecular Theory of Magnetism inside of all magnets, the tiny molecules that the magnet are made of, are all little tiny magnets in themselves, and that they are all lined up in a row. 

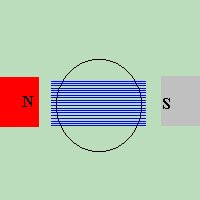
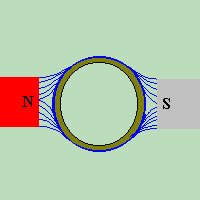
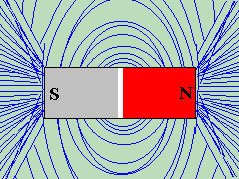 If we place a magnet beneath a piece of paper, and place iron filings on top
of the piece of paper, the result would look something like the example to the
right. The iron filings will arrange themselves to LOOK like the invisible
magnetic force which surrounds the magnet. This invisible magnetic force which
exists in the air or space around the magnet, is known as a
MAGNETIC FIELD
, and the lines are called
MAGNETIC LINES OF FORCE
.
If we place a magnet beneath a piece of paper, and place iron filings on top
of the piece of paper, the result would look something like the example to the
right. The iron filings will arrange themselves to LOOK like the invisible
magnetic force which surrounds the magnet. This invisible magnetic force which
exists in the air or space around the magnet, is known as a
MAGNETIC FIELD
, and the lines are called
MAGNETIC LINES OF FORCE
.
|
[COURSE INDEX] [ELECTRONICS GLOSSARY] [HOME]
| Otherwise - please click to visit an advertiser so they know you saw their ad! |
