


Tube Theory - The Diode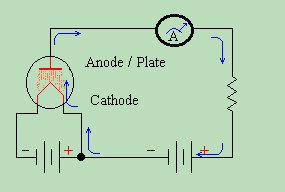
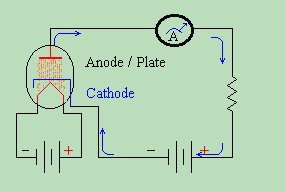
Both of the schematics above show the operation of a diode tube. Now let's study a little about the theory of its use. While not the only use for a diode, the most common use is that of RECTIFICATION . Rectification is just a big fancy word for changing Alternating Current into Direct Current. A RECTIFIER turns AC into DC, and a diode is an excellent rectifier. This is because it only allows electrical current to pass through the plate circuit in one direction. Let us examine what happens when we apply an alternating current to the plate circuit. 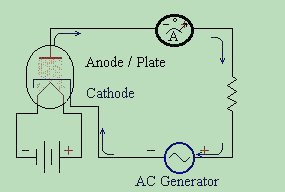 We replace the battery in the plate circuit with an AC generator. The AC
generator creates electrical voltage which swings from a positive to a negative
potential each cycle. When the generator's terminal on the cathode side swings
negative, the the one on the plate side swings positive. This energises the
tube such that the cathode is negative and the plate is positive. The
electrons floating about in the electron cloud are repelled by the negative
cathode. At the same time, they are attracted to the positive potential of the
plate. For this reason, they travel through the vacuum to the plate. These
electrons then go through the Ammeter, making it read current flow, and
continue onward to the load resistor. Finally they reach the most positive
point in the circuit - the positive terminal of the battery. They are drawn to
the positive, much like a South pole magnet is drawn to a North pole magnet,
and they will move toward each other until they meet.
We replace the battery in the plate circuit with an AC generator. The AC
generator creates electrical voltage which swings from a positive to a negative
potential each cycle. When the generator's terminal on the cathode side swings
negative, the the one on the plate side swings positive. This energises the
tube such that the cathode is negative and the plate is positive. The
electrons floating about in the electron cloud are repelled by the negative
cathode. At the same time, they are attracted to the positive potential of the
plate. For this reason, they travel through the vacuum to the plate. These
electrons then go through the Ammeter, making it read current flow, and
continue onward to the load resistor. Finally they reach the most positive
point in the circuit - the positive terminal of the battery. They are drawn to
the positive, much like a South pole magnet is drawn to a North pole magnet,
and they will move toward each other until they meet.
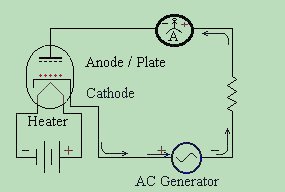 When, however, the AC generator reverses (alternates) its polarity, such that
the generator's cathode side terminal swings positive, and the plate side
swings negative - look what
When, however, the AC generator reverses (alternates) its polarity, such that
the generator's cathode side terminal swings positive, and the plate side
swings negative - look what
happens !! With the cathode being positive, the electron cloud collapses, and no electrons are present to cross over to the plate. Because the plate is not heated to thermonic emission, it does not radiate electrons, and so will not allow current to flow. Current flow stops at the plate. Therefore, in a vacuum tube, ELECTRICITY CAN ONLY FLOW IN ONE DIRECTION 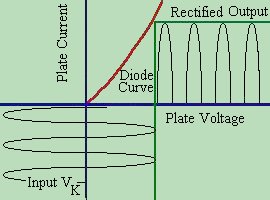 If we draw a graph, indicating voltages fed to the cathode vs current flow
monitored at the plate, we will see a pattern. Electricity only flows on the
positive cycle of the AC waveform. While the input swings both positive and
negative, the output fluctuates from 0 volts to some positive number of volts.
In effect, the input is Alternating between positive and negative (AC) but the
output is positive only (DC). We say that the output of the tube has been
rectified.
It is, however pulses of DC, and for most general purposes, useless until we
clean it up. This IS however, the basis of EVERY POWER SUPPLY in every piece
of electronic equipment you own.
If we draw a graph, indicating voltages fed to the cathode vs current flow
monitored at the plate, we will see a pattern. Electricity only flows on the
positive cycle of the AC waveform. While the input swings both positive and
negative, the output fluctuates from 0 volts to some positive number of volts.
In effect, the input is Alternating between positive and negative (AC) but the
output is positive only (DC). We say that the output of the tube has been
rectified.
It is, however pulses of DC, and for most general purposes, useless until we
clean it up. This IS however, the basis of EVERY POWER SUPPLY in every piece
of electronic equipment you own.
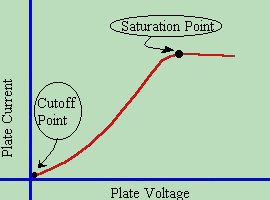 The Characteristic Curve of the diode is found by applying several different
voltage levels, and measuring plate voltages vs. plate current. We note that
below a certain plate voltage, ( in this case 0 volts ) no plate current flows.
The minimum point at which the tube no longer operates is called the
CUTOFF POINT
. Above a certain plate voltage, additional plate voltage has very little
effect in increasing the plate current. The maximum point where raising the
plate voltage no longer increases current is called the
SATURATION POINT
.
The Characteristic Curve of the diode is found by applying several different
voltage levels, and measuring plate voltages vs. plate current. We note that
below a certain plate voltage, ( in this case 0 volts ) no plate current flows.
The minimum point at which the tube no longer operates is called the
CUTOFF POINT
. Above a certain plate voltage, additional plate voltage has very little
effect in increasing the plate current. The maximum point where raising the
plate voltage no longer increases current is called the
SATURATION POINT
.
|
| (On The Following Indicator... PURPLE will indicate your current location) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 | 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 | 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 |
| 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 | 56 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 60 | 61 | 62 | 63 | 64 | 65 | 66 | 67 | 68 | 69 | 70 | 71 | 72 | 73 | 74 | 75 |
| Otherwise - please click to visit an advertiser so they know you saw their ad! |
